The global GHG emissions trend has increased since the beginning of the 21st century in comparison to the three previous decades, mainly due to the increase in CO2 emissions from China and the other emerging economies. As a result, the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases substantially increased enhancing the natural greenhouse effect, which may negatively affect the life on the Earth. These issues are internationally addressed in the framework of UNFCCC; countries are developing national emissions inventories and propose/implement actions to mitigate GHG emissions. CO2 emissions, which are the main responsible for global warming are still increasing at world level despite climate change mitigation agreements. However, CO2 emissions within the EU28 have decreased in the last two decades. Human related activities largely influence the total CO2 emissions – particularly, power generation and road transport but also emissions from combustion in the residential and commercial sectors play a key role. Despite decreasing trends for total EU28 CO2 emissions, CO2 emissions per capita within the EU28 are still higher than the world average value.
Read more at https://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu/overview.php?v=booklet2019
Ideo Concepts – Hong Kong, Auckland and Singapore provide website solutions are included: Sourcing Solution, Sourcing Agents, Exporters and Buying Offices, E-commerce Solutions, Corporate Website Solutions, Corporate Web Application Development, Web Applications Development, On-line Applications, Web Solutions Development, Database Applications, Integration and Application Hosting & Support.
Tuesday, December 31, 2019
Wednesday, December 25, 2019
China, US biggest carbon polluters, study finds
The world continues to increase the amount of heat-trapping carbon dioxide it pumps into the air, but it’s not rising as fast as in the previous couple years.
Led by big jumps from China and India, the world is projected to spew 40.57 billion tons (36.8 billion metric tons) of carbon dioxide into the air in 2019. That is up nearly 255 million tons (231 million metric tons) from 2018, according to two scientific studies released Tuesday.
Read more at http://www.thestandard.com.hk/breaking-news.php?id=137976&sid=6
Led by big jumps from China and India, the world is projected to spew 40.57 billion tons (36.8 billion metric tons) of carbon dioxide into the air in 2019. That is up nearly 255 million tons (231 million metric tons) from 2018, according to two scientific studies released Tuesday.
Read more at http://www.thestandard.com.hk/breaking-news.php?id=137976&sid=6
Tuesday, December 24, 2019
EMS (Energy Management System) can manage greenhouse gas accounting, reporting and management
The emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases due to power generation, transportation and other industrial / commercial activities are contributing to climate change and environmental impacts worldwide. EMS (Energy Management System) can manage greenhouse gas accounting, reporting and management in Hong Kong, China, Singapore, New Zealand and UK.
Wednesday, December 18, 2019
Studio Retail has announced that it is selling its Findel Education unit to Wakefield City Council for £50 million.
Studio Retail has announced that it is selling its Findel Education unit to Wakefield City Council for £50 million.
Creating an AI can be five times worse for the planet than a car
Training artificial intelligence is an energy intensive process. New estimates suggest that the carbon footprint of training a single AI is as much as 284 tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent – five times the lifetime emissions of an average car.
Read more: https://www.newscientist.com/article/2205779-creating-an-ai-can-be-five-times-worse-for-the-planet-than-a-car/
Friday, December 13, 2019
Li Ka Shing Foundation Processes 'Instant Relief Fund' via Google Cloud AI; Applications in 8 Mins on Avg.
The Li Ka Shing Foundation is embracing technology and using Google Cloud AI to facilitate application for Crunch Time Instant Relief Fund for eligible SMEs. The entire application and review process is completed within a matter of days, as all data are processed online automatically.
60% of applications were submitted via a mobile device and it takes just five seconds for Google Cloud Vision AI to process the text in each image. Each application can be submitted within eight minutes and The Foundation was able to process over 43,000 applications within the first 3 weeks, said Lucy Werner, Head of Google Cloud Hong Kong.
Source: https://www.aastocks.com/en/stocks/analysis/stock-aafn-con/00001/NOW.980301/hk-stock-news
60% of applications were submitted via a mobile device and it takes just five seconds for Google Cloud Vision AI to process the text in each image. Each application can be submitted within eight minutes and The Foundation was able to process over 43,000 applications within the first 3 weeks, said Lucy Werner, Head of Google Cloud Hong Kong.
Source: https://www.aastocks.com/en/stocks/analysis/stock-aafn-con/00001/NOW.980301/hk-stock-news
Monday, December 2, 2019
EU bank to focus solely on clean energy sources starting in 2022
(CNN Business)The European Investment Bank (EIB) announced Thursday that it will end financing for fossil fuel energy projects at the end of 2021, adding in a statement that future financing will focus on accelerating innovations in clean energy.
"We will stop financing fossil fuels and we will launch the most ambitious climate investment strategy of any public financial institution anywhere," EIB President Werner Hoyer said Thursday.
The EIB is the European Union's lending arm. Its new energy lending policy will "unlock 1 trillion euros of climate action and environmental sustainable investment" in order to enable energy decarbonisation, and meet a 32% renewable energy share throughout the European Union by 2030.
"Climate is the top issue on the political agenda of our time...The EU bank has been Europe's climate bank for many years. Today it has decided to make a quantum leap in its ambition," Hoyer added.
Continue reading at https://edition.cnn.com/2019/11/14/intl_business/eu-funding-fossil-fuel-projects/index.html
"We will stop financing fossil fuels and we will launch the most ambitious climate investment strategy of any public financial institution anywhere," EIB President Werner Hoyer said Thursday.
The EIB is the European Union's lending arm. Its new energy lending policy will "unlock 1 trillion euros of climate action and environmental sustainable investment" in order to enable energy decarbonisation, and meet a 32% renewable energy share throughout the European Union by 2030.
"Climate is the top issue on the political agenda of our time...The EU bank has been Europe's climate bank for many years. Today it has decided to make a quantum leap in its ambition," Hoyer added.
Continue reading at https://edition.cnn.com/2019/11/14/intl_business/eu-funding-fossil-fuel-projects/index.html
Thursday, October 10, 2019
WWF-Hong Kong’s view on Long-term Decarbonisation Strategy
This paper sets out WWF-Hong Kong’s (WWF) views on an all-rounded and feasible
long-term decarbonisation strategy for Hong Kong. In order to achieve the goal of
limiting global heating to 1.5°C, all 7 key elements below should be adopted and
implemented by policymakers:
1. HKSAR Government to show strong leadership and determination to
limit global heating to 1.5°C through setting a legally-bound, sciencebased target by 2022
The Chief Executive should lead all government departments, public bodies,
and agencies to develop and commit to legally-bound, science-based targets
aimed at limiting global heating to 1.5°C.
2. Meet 10% renewable energy (RE) target by 2030, achieve net zero
emission by 2048 through global and regional cooperation
It is necessary to innovate, diversify, and magnify the application of solar PV
technology. In the long-term, explore global and regional cooperation for RE
trade and avoid trade-offs. The Government should not construct new
additional gas-fired generating units in the next Scheme of Control
agreement. Avoid further sourcing of nuclear energy. Stricter rules should be
applied to the application of bioenergy.
3. Realise a 50% energy saving improvement roadmap to 2050
It is essential to establish a mandatory climate change mitigation and
adaptation building scheme to all new building and introduce a carbon
budgeting mechanism for existing buildings.
4. Introduce decarbonisation financing scheme and put a true cost on
carbon
Replicate energy efficiency and renewable energy projects within government
properties to open spaces and privately-owned buildings. Open for public
acquisition and allocate complementary shares to the public. Conduct studies
on the economic, social, and financial implications of the climate crisis, and
design a progressive carbon charging system.
3
5. Establish a global extensive native-species reforestation program for
extant grassland areas
Reforestation can contribute to carbon sequestration and make Hong Kong
more carbon neutral. Subtropical forests can sequester 10 to 30 metric tonnes
of carbon per hectare. It can also reduce erosion and bolster freshwater
supplies.
6. Rethink urban planning and transform Hong Kong into one of Asia’s
most walkable cities
Mandate district cooling systems in the urban planning process. Develop
underground pedestrian commute paths to promote a low carbon lifestyle.
Phase out sales of petrol and diesel cars by 2030. Roll out a “no-car-day” in
city centers. Provide incentives for electric vehicle acquisition and operation.
7. Healthy and wealthy, people-centric strategy
It is essential to put people at the heart of the decarbonisation policies. Set
up a public engagement team to regularly collect public feedback on longterm strategy. Introduce a compulsory climate crisis course for kindergarten,
primary and secondary school. Promote home office, community working
center and community-based job creation to avoid long distance commute.
Avoid inequalities when forming a new scheme.
Source: https://d3q9070b7kewus.cloudfront.net/downloads/wwf_submission_on_long_term_decarbonisation_final.pdf
long-term decarbonisation strategy for Hong Kong. In order to achieve the goal of
limiting global heating to 1.5°C, all 7 key elements below should be adopted and
implemented by policymakers:
1. HKSAR Government to show strong leadership and determination to
limit global heating to 1.5°C through setting a legally-bound, sciencebased target by 2022
The Chief Executive should lead all government departments, public bodies,
and agencies to develop and commit to legally-bound, science-based targets
aimed at limiting global heating to 1.5°C.
2. Meet 10% renewable energy (RE) target by 2030, achieve net zero
emission by 2048 through global and regional cooperation
It is necessary to innovate, diversify, and magnify the application of solar PV
technology. In the long-term, explore global and regional cooperation for RE
trade and avoid trade-offs. The Government should not construct new
additional gas-fired generating units in the next Scheme of Control
agreement. Avoid further sourcing of nuclear energy. Stricter rules should be
applied to the application of bioenergy.
3. Realise a 50% energy saving improvement roadmap to 2050
It is essential to establish a mandatory climate change mitigation and
adaptation building scheme to all new building and introduce a carbon
budgeting mechanism for existing buildings.
4. Introduce decarbonisation financing scheme and put a true cost on
carbon
Replicate energy efficiency and renewable energy projects within government
properties to open spaces and privately-owned buildings. Open for public
acquisition and allocate complementary shares to the public. Conduct studies
on the economic, social, and financial implications of the climate crisis, and
design a progressive carbon charging system.
3
5. Establish a global extensive native-species reforestation program for
extant grassland areas
Reforestation can contribute to carbon sequestration and make Hong Kong
more carbon neutral. Subtropical forests can sequester 10 to 30 metric tonnes
of carbon per hectare. It can also reduce erosion and bolster freshwater
supplies.
6. Rethink urban planning and transform Hong Kong into one of Asia’s
most walkable cities
Mandate district cooling systems in the urban planning process. Develop
underground pedestrian commute paths to promote a low carbon lifestyle.
Phase out sales of petrol and diesel cars by 2030. Roll out a “no-car-day” in
city centers. Provide incentives for electric vehicle acquisition and operation.
7. Healthy and wealthy, people-centric strategy
It is essential to put people at the heart of the decarbonisation policies. Set
up a public engagement team to regularly collect public feedback on longterm strategy. Introduce a compulsory climate crisis course for kindergarten,
primary and secondary school. Promote home office, community working
center and community-based job creation to avoid long distance commute.
Avoid inequalities when forming a new scheme.
Source: https://d3q9070b7kewus.cloudfront.net/downloads/wwf_submission_on_long_term_decarbonisation_final.pdf
Wednesday, October 9, 2019
Reductions of China national emission improved air quality in past 3 years
The reductions are important in helping to control China’s national emissions which could lead to an improvement in air quality and considerable health benefits.
A team of experts from the UK and China analysed emissions from coal, oil, natural gas and biomass power plants, with a focus on coal-fired power plants as the major contributors to ambient air pollution.
The study, published today in Nature Energy, analysed data from 2014, when China introduced the ambitious Ultra-Low Emissions (ULE) Standards Policy for renovating coal-fired power stations to limit air pollutant emissions, to 2017.
The team found that between 2014 and 2017, China’s annual power plant emissions of sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide and particulate matter dropped by 65%, 60% and 72% each year respectively from 2.21, 3.11 and 0.52 million tonnes in 2014 to 0.77, 1.26 and 0.14 million tonnes in 2017, under the ULE standards policy.
Source: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/news/2019/oct/china-track-meet-its-ultra-low-emissions-goals-2020
Polluting emissions from Chinese thermal power plants declined significantly between 2014 and 2017, according to research involving UCL.
China is on track to meet its ultra-low emissions goals for 2020
A team of experts from the UK and China analysed emissions from coal, oil, natural gas and biomass power plants, with a focus on coal-fired power plants as the major contributors to ambient air pollution.
The study, published today in Nature Energy, analysed data from 2014, when China introduced the ambitious Ultra-Low Emissions (ULE) Standards Policy for renovating coal-fired power stations to limit air pollutant emissions, to 2017.
The team found that between 2014 and 2017, China’s annual power plant emissions of sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide and particulate matter dropped by 65%, 60% and 72% each year respectively from 2.21, 3.11 and 0.52 million tonnes in 2014 to 0.77, 1.26 and 0.14 million tonnes in 2017, under the ULE standards policy.
Source: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/news/2019/oct/china-track-meet-its-ultra-low-emissions-goals-2020
Polluting emissions from Chinese thermal power plants declined significantly between 2014 and 2017, according to research involving UCL.
China is on track to meet its ultra-low emissions goals for 2020
Tuesday, September 24, 2019
Sony, Microsoft, Stadia, and others join forces with United Nations to announce new climate change commitments
A more eco-friendly PS5. The PS5 to include a low power suspend mode to help reduce carbon emissions, Sony announces as part of new partnership with United Nations
Today, the United Nations has announced it is partnering with 21 companies in the video game industry to "harness the power of their platforms to take action in response to the climate crisis", as part of its new Playing for the Planet initiative.
The likes of Sony, Microsoft, Google Stadia, Ubisoft, and more have all pledged to the programme, announcing various initiatives to reduce their own corporate carbon footprint while simultaneously promoting awareness about the climate crisis through their medium.
Sony's President and CEO Jim Ryan, for example, has announced that the upcoming PS5, the next generation PlayStation console, will feature a "low power suspend mode" which could potentially save huge amounts of energy expenditure for its users around the world.
Microsoft is continuing to reach its aims of producing carbon neutral Xbox consoles, and plans to reduce its supply chain emissions by 20% in 2030, while Google Stadia is releasing a Sustainable Game Development Guide to help its partnered studios create games through greener processes.
Full story here: https://www.gamesradar.com/sony-microsoft-stadia-and-others-join-forces-with-united-nations-to-announce-new-climate-change-commitments-including-a-more-eco-friendly-ps5/
Today, the United Nations has announced it is partnering with 21 companies in the video game industry to "harness the power of their platforms to take action in response to the climate crisis", as part of its new Playing for the Planet initiative.
The likes of Sony, Microsoft, Google Stadia, Ubisoft, and more have all pledged to the programme, announcing various initiatives to reduce their own corporate carbon footprint while simultaneously promoting awareness about the climate crisis through their medium.
Sony's President and CEO Jim Ryan, for example, has announced that the upcoming PS5, the next generation PlayStation console, will feature a "low power suspend mode" which could potentially save huge amounts of energy expenditure for its users around the world.
Microsoft is continuing to reach its aims of producing carbon neutral Xbox consoles, and plans to reduce its supply chain emissions by 20% in 2030, while Google Stadia is releasing a Sustainable Game Development Guide to help its partnered studios create games through greener processes.
Full story here: https://www.gamesradar.com/sony-microsoft-stadia-and-others-join-forces-with-united-nations-to-announce-new-climate-change-commitments-including-a-more-eco-friendly-ps5/
Friday, August 30, 2019
Roads / Environment / Light vehicle emissions
The NTC began reporting on the carbon dioxide emissions of new cars and light commercial vehicles in 2009, to provide a transparent benchmark for how Australia’s new car emissions performance is tracking.
Light vehicle emissions
The NTC reports on the carbon dioxide emissions intensity of new cars and light commercial vehicle sales to provide a transparent benchmark for how Australia’s new car emission performance is tracking.
Key findings from our latest report:
In 2018 the national average carbon dioxide emissions intensity from new passenger and light commercial vehicles was 1 80.9 g/km. This is a 0.4 per cent improvement from 2017. This is the second lowest annual improvement since records started in 2002.
Consumer preferences are an important factor affecting the national average of carbon dioxide emissions intensity for new vehicles. If all Australians who purchased new vehicles in 2018 had purchased vehicles with best-in-class emissions, the national average carbon dioxide emissions intensity would have been reduced to 73 g/km, a 60 per cent reduction.
About 91 per cent of all new vehicle sales in 201 8 were from 15 makes. Of these 15 makes, Audi had the lowest corporate average emissions intensity (148 g/km), and Ford had the highest (216 g/km).
Light vehicle emissions
The NTC reports on the carbon dioxide emissions intensity of new cars and light commercial vehicle sales to provide a transparent benchmark for how Australia’s new car emission performance is tracking.
Key findings from our latest report:
In 2018 the national average carbon dioxide emissions intensity from new passenger and light commercial vehicles was 1 80.9 g/km. This is a 0.4 per cent improvement from 2017. This is the second lowest annual improvement since records started in 2002.
Consumer preferences are an important factor affecting the national average of carbon dioxide emissions intensity for new vehicles. If all Australians who purchased new vehicles in 2018 had purchased vehicles with best-in-class emissions, the national average carbon dioxide emissions intensity would have been reduced to 73 g/km, a 60 per cent reduction.
About 91 per cent of all new vehicle sales in 201 8 were from 15 makes. Of these 15 makes, Audi had the lowest corporate average emissions intensity (148 g/km), and Ford had the highest (216 g/km).
Source
California Greenhouse Gas Emissions for 2000 to 2017 Trends of Emissions and Other Indicators
The annual statewide greenhouse gas (GHG) emission inventory is an important tool in
tracking progress towards meeting statewide GHG goals. The inventory for 2017 shows that
California’s GHG emissions continue to decrease. In 2017, emissions from GHG emitting
activities statewide were 424 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent (MMTCO2e), 5 MMTCO2e
lower than 2016 levels and 7 MMTCO2e below the 2020 GHG Limit of 431 MMTCO2e.
Consistent with recent years, these reductions have occurred while California’s economy has
continued to grow and generate jobs. Compared to 2016, California’s GDP grew 3.6 percent
while the carbon intensity of its economy declined by 4.5 percent. The most notable highlights in
the inventory include:
• For the first time since California started to track GHG emissions, in-state and total
electricity generation from zero-GHG sources (for purposes of the GHG inventory,
these include solar, hydro, wind, and nuclear) exceeded generation from GHGemitting sources.
• The transportation sector remains the largest source of GHG emissions in the state,
but saw a 1 percent increase in emissions in 2017, the lowest growth rate over the
past 4 years.
• Emissions from all other sectors have remained relatively constant in recent years,
although emissions from high Global Warming Potential (GWP) gases have continued
to increase as they replace Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS) banned under the
1987 Montreal Protocol.
source: https://ww3.arb.ca.gov/cc/inventory/pubs/reports/2000_2017/ghg_inventory_trends_00-17.pdf
tracking progress towards meeting statewide GHG goals. The inventory for 2017 shows that
California’s GHG emissions continue to decrease. In 2017, emissions from GHG emitting
activities statewide were 424 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent (MMTCO2e), 5 MMTCO2e
lower than 2016 levels and 7 MMTCO2e below the 2020 GHG Limit of 431 MMTCO2e.
Consistent with recent years, these reductions have occurred while California’s economy has
continued to grow and generate jobs. Compared to 2016, California’s GDP grew 3.6 percent
while the carbon intensity of its economy declined by 4.5 percent. The most notable highlights in
the inventory include:
• For the first time since California started to track GHG emissions, in-state and total
electricity generation from zero-GHG sources (for purposes of the GHG inventory,
these include solar, hydro, wind, and nuclear) exceeded generation from GHGemitting sources.
• The transportation sector remains the largest source of GHG emissions in the state,
but saw a 1 percent increase in emissions in 2017, the lowest growth rate over the
past 4 years.
• Emissions from all other sectors have remained relatively constant in recent years,
although emissions from high Global Warming Potential (GWP) gases have continued
to increase as they replace Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS) banned under the
1987 Montreal Protocol.
source: https://ww3.arb.ca.gov/cc/inventory/pubs/reports/2000_2017/ghg_inventory_trends_00-17.pdf
Study: China may hit emission goals early
An international study has found that China is on track to meet its carbon emissions goals up to one decade early.
China, one of the first countries to sign the Paris Agreement on climate change, has pledged to halt the rise in carbon dioxide emissions by around 2030.
Researchers from China's Nanjing University, Tsinghua University, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Harvard University in the United States examined carbon dioxide emissions from 50 Chinese cities from 2000 to 2016 and found a close relationship between per capita emissions and per capita gross domestic product.
Those 50 cities account for about 35 percent of China's total carbon emissions and 51 percent of the country's GDP.
source: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/global/2019-08/27/content_37505778.htm
China, one of the first countries to sign the Paris Agreement on climate change, has pledged to halt the rise in carbon dioxide emissions by around 2030.
Researchers from China's Nanjing University, Tsinghua University, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Harvard University in the United States examined carbon dioxide emissions from 50 Chinese cities from 2000 to 2016 and found a close relationship between per capita emissions and per capita gross domestic product.
Those 50 cities account for about 35 percent of China's total carbon emissions and 51 percent of the country's GDP.
source: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/global/2019-08/27/content_37505778.htm
Wednesday, August 28, 2019
Huge carbon monoxide plume from Amazon rainforest fires
The devastating effect of the Amazon forest fires on our planet have been revealed in a NASA time series.
The images, created using data from NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard the Aqua satellite, show a giant carbon monoxide plume gathering over Brazil.
Source: https://www.mirror.co.uk/science/huge-carbon-monoxide-plume-amazon-19007167
The images, created using data from NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard the Aqua satellite, show a giant carbon monoxide plume gathering over Brazil.
Source: https://www.mirror.co.uk/science/huge-carbon-monoxide-plume-amazon-19007167
Thursday, August 15, 2019
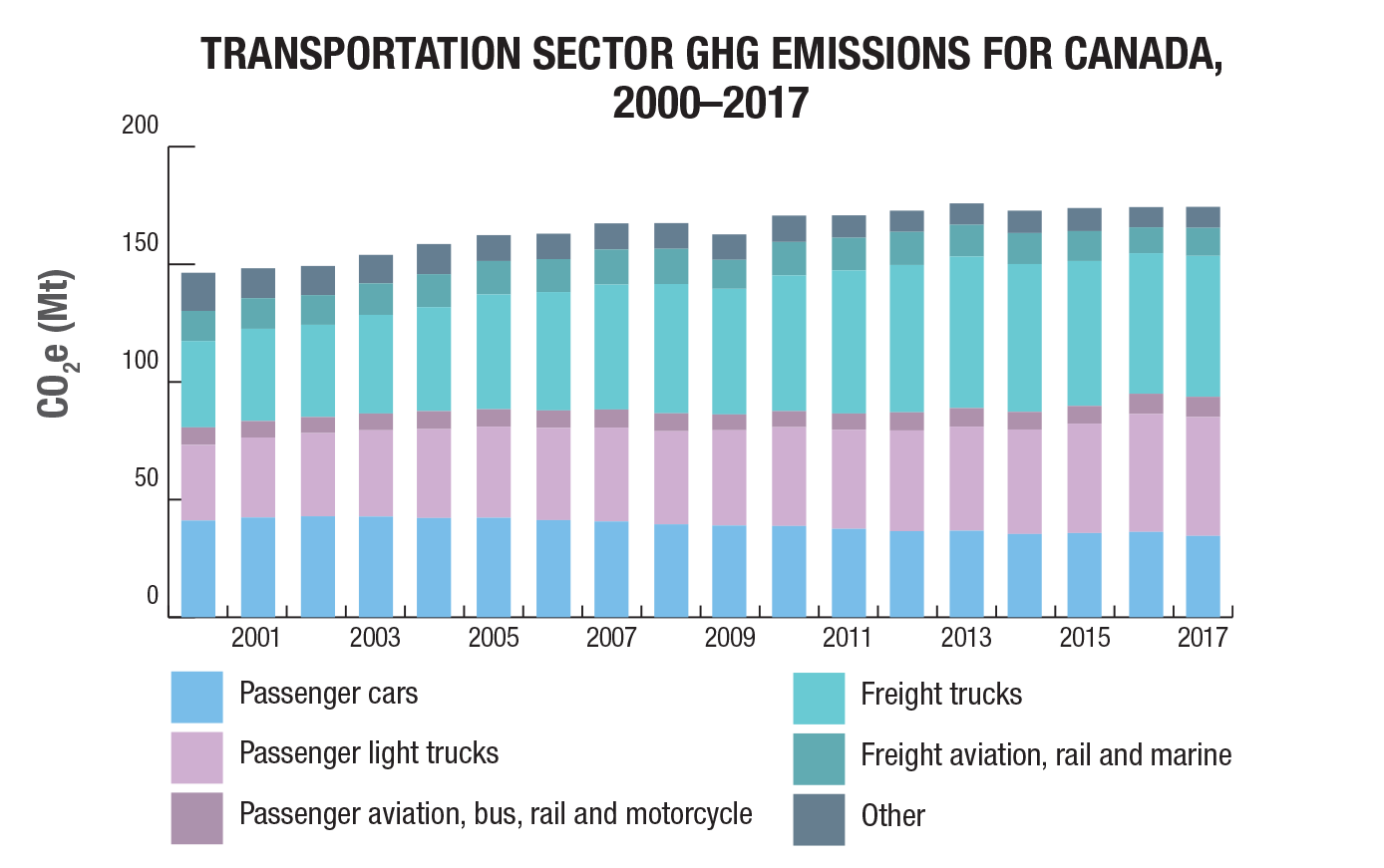
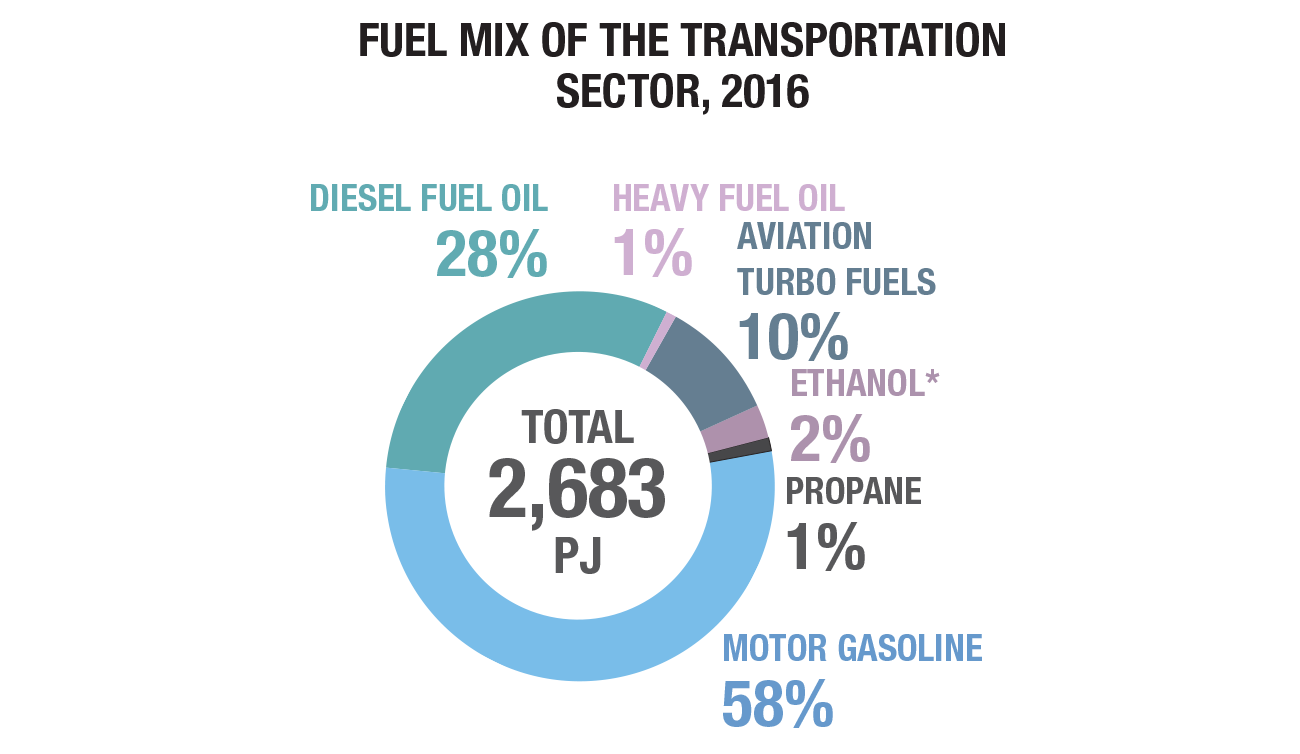
Transportation GHG emissions
GHG spotlight on transportation
Transportation GHG emissions have increased 19% from 2000 to 2017. Emissions from passenger light trucks and freight trucks have continued to rise due to an increased number of vehicles (especially light trucks and SUVs). Freight emissions have increased due to many factors including increasing trade and globalization, and online shopping.
Passenger transportation contributes 54% to total emissions, freight emissions are 41% of total and off-road is 5%.
Energy efficiency improvements in the transportation sector have saved Canadians 763 PJ of energy and almost $20.8 billion in energy costs in 2016.
Total transportation energy use increased 16% from 2000 to 2016.
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
Transportation GHG emissions have increased 19% from 2000 to 2017. Emissions from passenger light trucks and freight trucks have continued to rise due to an increased number of vehicles (especially light trucks and SUVs). Freight emissions have increased due to many factors including increasing trade and globalization, and online shopping.
Passenger transportation contributes 54% to total emissions, freight emissions are 41% of total and off-road is 5%.
Energy efficiency improvements in the transportation sector have saved Canadians 763 PJ of energy and almost $20.8 billion in energy costs in 2016.
Total transportation energy use increased 16% from 2000 to 2016.
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
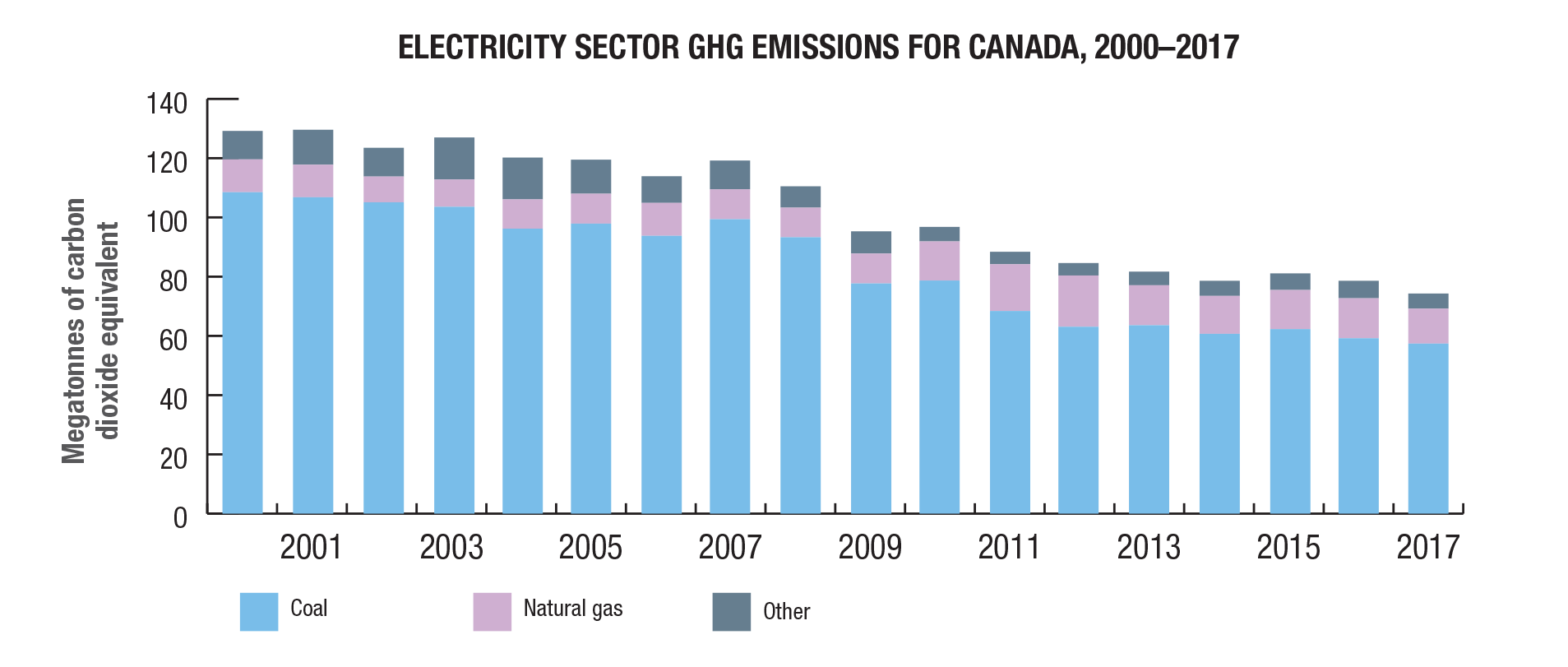
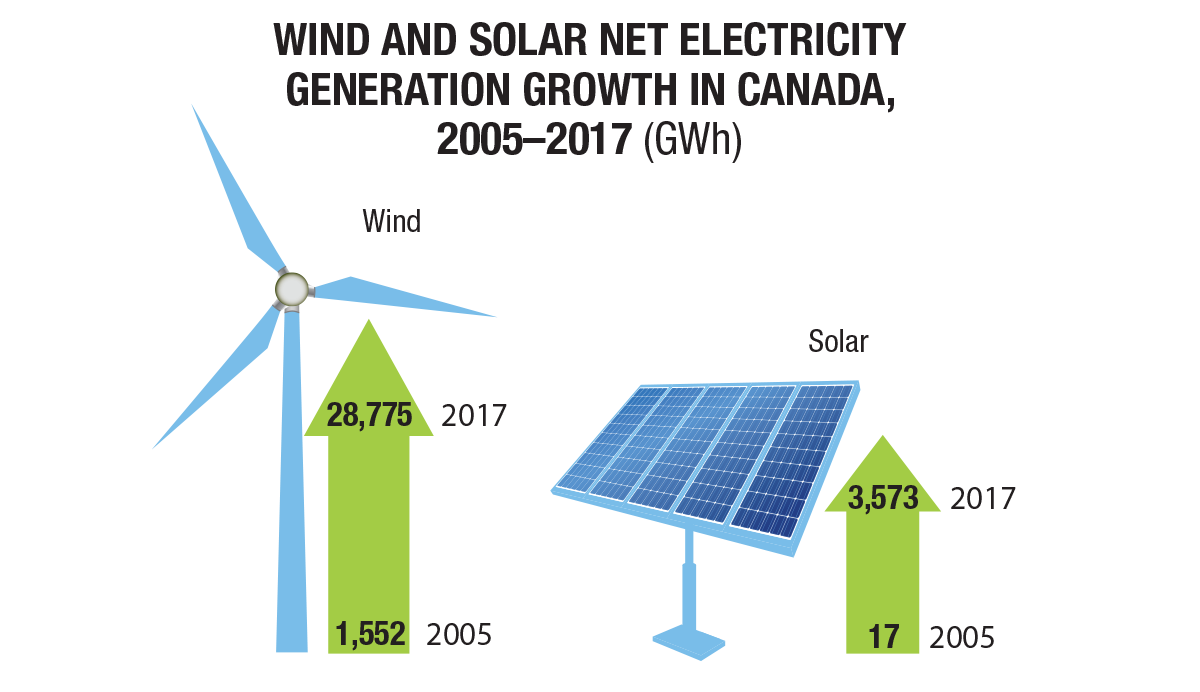
Total electricity emissions / GHG emissions on electricity
GHG spotlight on electricity
Despite accounting for less than 9% of total electricity generation, coal was responsible for 77% of electricity related GHG emissions in 2017. Total electricity emissions decreased by 42% from 2000 to 2017 due to increased generation from non-emitting sources.
Renewable electricity generation has increased 18% between 2010 and 2017, with solar and wind having largest growth.
In 2017, almost 82% of electricity in Canada came from non-GHG emitting sources. Hydro made up 60%, nuclear 15%, and other renewables the remaining 7%.
Renewable energy sources make up 2/3’s of Canada’s electricity mix. Renewable electricity generation has increased 18% between 2010 and 2017, with solar and wind having largest growth.
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
Despite accounting for less than 9% of total electricity generation, coal was responsible for 77% of electricity related GHG emissions in 2017. Total electricity emissions decreased by 42% from 2000 to 2017 due to increased generation from non-emitting sources.
Renewable electricity generation has increased 18% between 2010 and 2017, with solar and wind having largest growth.
In 2017, almost 82% of electricity in Canada came from non-GHG emitting sources. Hydro made up 60%, nuclear 15%, and other renewables the remaining 7%.
Renewable energy sources make up 2/3’s of Canada’s electricity mix. Renewable electricity generation has increased 18% between 2010 and 2017, with solar and wind having largest growth.
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
Wednesday, August 14, 2019
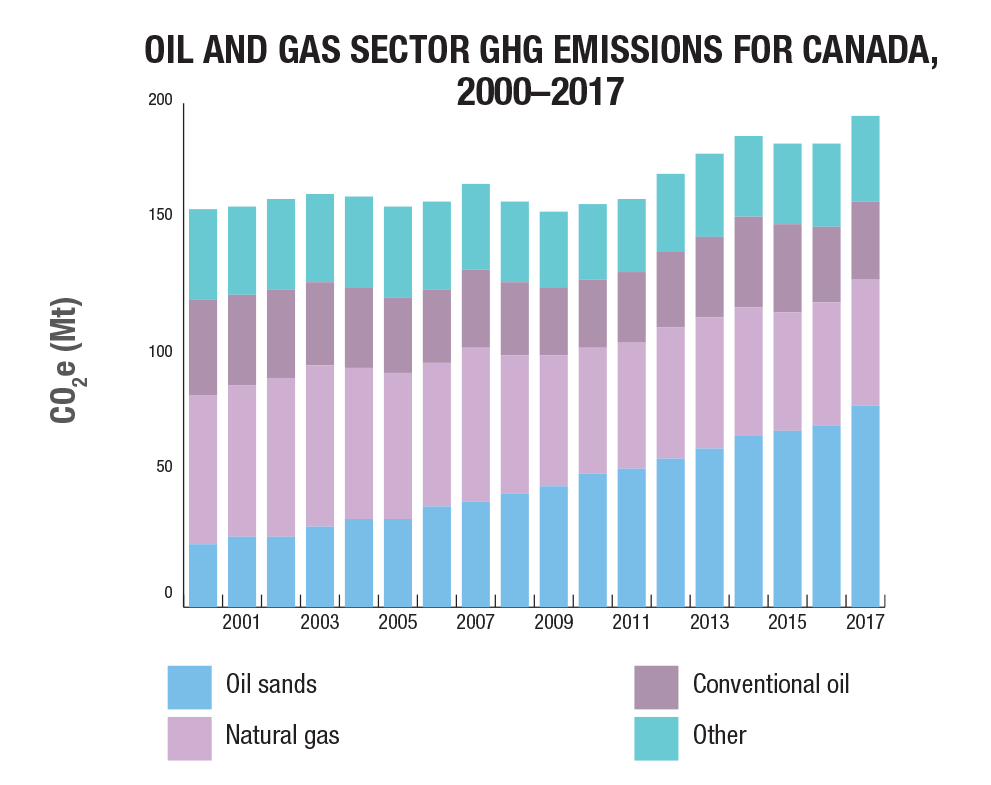
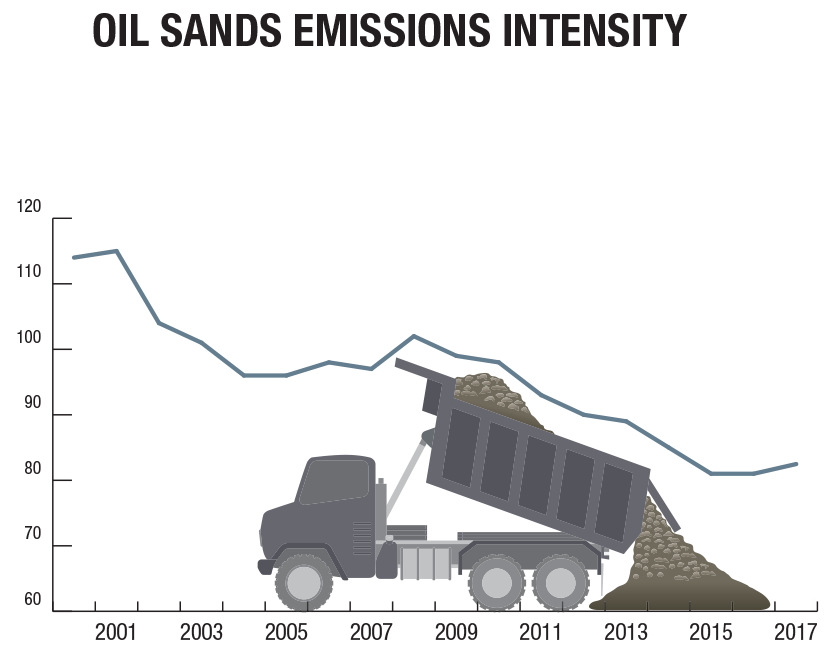
GHG spotlight on oil and gas
GHG spotlight on oil and gas
GHG emissions from oil and gas production have gone up 23% between 2005 and 2017, largely from increased oil sands production, particularly in-situ extraction.
The Government of Canada has committed to reducing methane emissions from the oil and gas sector by 40% to 45% from 2012 levels by 2025. New regulations limiting methane emissions from fugitive sources such as leaks and venting will apply to the oil and gas sector beginning in 2020.
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
GHG emissions from oil and gas production have gone up 23% between 2005 and 2017, largely from increased oil sands production, particularly in-situ extraction.
The Government of Canada has committed to reducing methane emissions from the oil and gas sector by 40% to 45% from 2012 levels by 2025. New regulations limiting methane emissions from fugitive sources such as leaks and venting will apply to the oil and gas sector beginning in 2020.
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
Energy use and greenhouse gas emissions
Energy use and greenhouse gas emissions
A wide variety of factors have an influence on the level of GHG emissions in Canada. Globally, about 78% of GHG emissions from human activity are from the production and consumption of energy. This includes activities such as using gasoline for transportation, non-renewable electricity production, oil and gas production, and heating and cooling of buildings.
In Canada, over 81% of emissions come from energy. Canadians use more energy due to our extreme temperatures, vast landscape and dispersed population.
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
A wide variety of factors have an influence on the level of GHG emissions in Canada. Globally, about 78% of GHG emissions from human activity are from the production and consumption of energy. This includes activities such as using gasoline for transportation, non-renewable electricity production, oil and gas production, and heating and cooling of buildings.
In Canada, over 81% of emissions come from energy. Canadians use more energy due to our extreme temperatures, vast landscape and dispersed population.
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
Energy and Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs) | Natural Resources Canada
Energy and Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs)
Protecting the environment and growing the economy go hand in hand. Taking action on climate change means reducing emissions and increasing climate resilience, while helping Canada diversify its economy and generate well-paying jobs.
Key Facts
In 2017, 82% of electricity in Canada came from non-GHG emitting sources
Energy consumption grew by 26% between 1990 and 2016
Energy efficiency improved by 31% between 1990 and 2016
Investment in clean energy technology was over $3.3 billion in 2017
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
Protecting the environment and growing the economy go hand in hand. Taking action on climate change means reducing emissions and increasing climate resilience, while helping Canada diversify its economy and generate well-paying jobs.
Key Facts
In 2017, 82% of electricity in Canada came from non-GHG emitting sources
Energy consumption grew by 26% between 1990 and 2016
Energy efficiency improved by 31% between 1990 and 2016
Investment in clean energy technology was over $3.3 billion in 2017
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-ghgs/20063#L1
Tuesday, August 6, 2019
can’t expand airports after declaring a climate emergency – let’s shift to low-carbon transport instead
The world may finally be waking to the reality of the climate and ecological crisis, after 30 years of inaction. But while the UK parliament has declared a climate and ecological emergency, ongoing plans for airport expansions suggest we’re flying full-speed towards crisis rather than away from it.
Globally, greenhouse gas emissions from aviation are rising rapidly, and set to further escalate. Passenger numbers are rising far too fast for efficiency improvements and alternative technologies, such as electric or biofuel-powered engines, to keep up. What’s worse, the climate impact of flights is two to three times larger than their CO₂ emissions alone, due to the release of nitrogen oxides – powerful greenhouse gases – and the contrails planes leave in their wake which trap even more heat in the atmosphere. The aviation industry has also evaded fuel taxes, emissions regulations, and is often completely omitted in emissions accounting.
This is particularly important as cities are setting targets to reduce their carbon emissions. While many of these cities have airports, their climate strategies tend to focus on the emissions released within the city’s boundaries and from their electricity use. They don’t account for emissions from imported goods and services that are consumed in the city but produced elsewhere, nor from flights through their airports. Any emissions from residents travelling outside the city are generally omitted.
Source: https://theconversation.com/we-cant-expand-airports-after-declaring-a-climate-emergency-lets-shift-to-low-carbon-transport-instead-120740
Globally, greenhouse gas emissions from aviation are rising rapidly, and set to further escalate. Passenger numbers are rising far too fast for efficiency improvements and alternative technologies, such as electric or biofuel-powered engines, to keep up. What’s worse, the climate impact of flights is two to three times larger than their CO₂ emissions alone, due to the release of nitrogen oxides – powerful greenhouse gases – and the contrails planes leave in their wake which trap even more heat in the atmosphere. The aviation industry has also evaded fuel taxes, emissions regulations, and is often completely omitted in emissions accounting.
This is particularly important as cities are setting targets to reduce their carbon emissions. While many of these cities have airports, their climate strategies tend to focus on the emissions released within the city’s boundaries and from their electricity use. They don’t account for emissions from imported goods and services that are consumed in the city but produced elsewhere, nor from flights through their airports. Any emissions from residents travelling outside the city are generally omitted.
Source: https://theconversation.com/we-cant-expand-airports-after-declaring-a-climate-emergency-lets-shift-to-low-carbon-transport-instead-120740
Monday, August 5, 2019
The Relationship Between Carbon Dioxide Emissions and Economic Growth
Aims: to understand past relationships between
national CO2 emissions and GDP to help inform current
debates about emission projections
Datasets considered:
– International Energy Agency
– Energy Information Administration (US DOE)
– CDIAC (US Oak Ridge)
– WRI CAIT
No major inconsistencies observed, EIA accessible for
general trend analysis, CDIAC and CAIT for data since
1950, WRI CAIT most complete for cross-comparisons
Population is an important factors; all comparisons
analysed on per-capita basis
Source: https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/the-relationship-between-carbon-dioxide-emissions-and-economic-growth/?v=69e1aafeccc5
national CO2 emissions and GDP to help inform current
debates about emission projections
Datasets considered:
– International Energy Agency
– Energy Information Administration (US DOE)
– CDIAC (US Oak Ridge)
– WRI CAIT
No major inconsistencies observed, EIA accessible for
general trend analysis, CDIAC and CAIT for data since
1950, WRI CAIT most complete for cross-comparisons
Population is an important factors; all comparisons
analysed on per-capita basis
Source: https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/the-relationship-between-carbon-dioxide-emissions-and-economic-growth/?v=69e1aafeccc5
Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Hong Kong
Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Hong Kong
Greenhouse gas emissions by sector
Greenhouse gas emissions and carbon intensity
Greenhouse gas emission trends
Greenhouse gas emissions by sector
Greenhouse gas emissions and carbon intensity
Greenhouse gas emission trends
按排放源劃分的香港溫室氣體排放量
Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Hong Kong by Sector
溫室氣體排放量 (千公噸二氧化碳當量)
Greenhouse gas emissions (in kilotonnes CO2-e)
能源
Energy
廢棄物
Waste
工業過程及產品使用
Industrial Processes and Product Use
農業、林業及其他土地利用
Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use
發電#
Electricity
Generation#
運輸
Transport
其它燃料耗用
Other End Use of Fuel@
1990 年至 2017 年香港溫室氣體排放趨勢
Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends of Hong Kong from 1990–2017
香港的溫室氣體排放量及碳強度
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Carbon Intensity in Hong Kong
年份
Year
溫室氣體排放總量
(千公噸二氧化碳當量)
Total GHG emissions
(kilotonnes CO2-e)
人均排放
(公噸二氧化碳當量)
Per capita emissions
(tonnes CO2-e)
碳強度
(千克二氧化碳當量/港元本地生產總值)
Carbon Intensity
(kg CO2-e per HK Dollar GDP)
Friday, August 2, 2019
IDEO CONCEPTS launches emission data management system EMS
The online data management system will help listed companies with GHG emission requirements. The new greenhouse gas (GHG) online data management system supports data collection, data transformation, data report creation. User upload collected data directly into web-based EMS. Emission calculation will automatically generate report data based on pre-configured annually emission factors from different providers/countries. FREE guideline is provided during the import process.
Finnlines calculated passenger-specific route CO2 emissions
Finnlines calculated passenger-specific route CO2 emissions – Finnlines’ vessels are an eco-friendly choice for passengers
Passenger-specific carbon-dioxide figures for 2018 have been calculated on Finnlines’ passenger routes, Naantali–Kapellskär, Malmö–Travemünde and Helsinki–Travemünde. The figures will be updated on a yearly basis and this will be the base for future calculations.
International legislation and Finnlines’ figures
The EU regulation on the monitoring, reporting and verification of CO2 emissions (MRV, EU 2015/757, EN 16258) became fully effective in 2018. Globally, IMO’s similar Data Collection System will start in 2019.
The Finnlines’ passenger-specific route figures are calculated on the basis of MRV data for 2018 verified by the authorities. Finnlines’ figures have been verified by official certification society.
Finnlines’ ro-pax vessels carry both passengers and freight, and thus the total annual fuel and emission data is divided between these categories. The MRV standard (EN 16258) allows to select between two methods: the mass and area method. Since Finnlines’ operations are mostly concentrated in cargo and freight, it is logical that Finnlines uses the mass method where the freight / passenger ratio is allocated annually according to carried freight and passenger.
The total CO2 emissions of the Finnlines’ fleet have reduced by approximately 30% in 2018 compared to 2008. Route-specific reductions can even be more due to better capacity utilisation.
In 2018, CO2 emissions per passenger on routes:
Naantali–Kapellskär was 13–14 kg CO2/passenger (MS Finnswan, MS Finnfellow)
Malmö–Travemünde was 15–16 kg CO2/passenger (MS Europalink, MS Finnpartner, MS Finntrader)
Helsinki–Travemünde was 69–79 kg CO2/passenger (MS Finnlady, MS Finnmaid, MS Finnstar).
Differences are due to passenger numbers and, for example, weather conditions and route choices.
Clear emission goals & new eco-efficient ships
continue reading at https://seanews.co.uk/news/global-events/finnlines-calculated-passenger-specific-route-co2-emissions/
Passenger-specific carbon-dioxide figures for 2018 have been calculated on Finnlines’ passenger routes, Naantali–Kapellskär, Malmö–Travemünde and Helsinki–Travemünde. The figures will be updated on a yearly basis and this will be the base for future calculations.
International legislation and Finnlines’ figures
The EU regulation on the monitoring, reporting and verification of CO2 emissions (MRV, EU 2015/757, EN 16258) became fully effective in 2018. Globally, IMO’s similar Data Collection System will start in 2019.
The Finnlines’ passenger-specific route figures are calculated on the basis of MRV data for 2018 verified by the authorities. Finnlines’ figures have been verified by official certification society.
Finnlines’ ro-pax vessels carry both passengers and freight, and thus the total annual fuel and emission data is divided between these categories. The MRV standard (EN 16258) allows to select between two methods: the mass and area method. Since Finnlines’ operations are mostly concentrated in cargo and freight, it is logical that Finnlines uses the mass method where the freight / passenger ratio is allocated annually according to carried freight and passenger.
The total CO2 emissions of the Finnlines’ fleet have reduced by approximately 30% in 2018 compared to 2008. Route-specific reductions can even be more due to better capacity utilisation.
In 2018, CO2 emissions per passenger on routes:
Naantali–Kapellskär was 13–14 kg CO2/passenger (MS Finnswan, MS Finnfellow)
Malmö–Travemünde was 15–16 kg CO2/passenger (MS Europalink, MS Finnpartner, MS Finntrader)
Helsinki–Travemünde was 69–79 kg CO2/passenger (MS Finnlady, MS Finnmaid, MS Finnstar).
Differences are due to passenger numbers and, for example, weather conditions and route choices.
Clear emission goals & new eco-efficient ships
continue reading at https://seanews.co.uk/news/global-events/finnlines-calculated-passenger-specific-route-co2-emissions/
Wednesday, July 24, 2019
Korea helps developing countries learn about carbon emissions
The Korean environment ministry on Monday began a four-week program in Yeouido, Seoul, for representatives from 33 developing countries on how to reduce carbon emissions.
Jointly hosted by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the "Program on Greenhouse Gases" invited 33 environment officials, from countries in Asia, Africa, South America and Oceania.
The ministry's Greenhouse Gas Inventory and Research Center selected the participants through screening 348 candidates from 84 countries based on the candidates' academic and employment histories and IT skills.
The instructors are three Koreans and six from overseas, including those from the UNFCCC, the Austrian environment ministry and the RWA Group, an international group of experts in waste management, resource and energy efficiency.
The program teaches about measurement, reporting and verification (MRV) of carbon emissions in the sectors of energy, manufacturing, agriculture and waste; guidelines from the intergovernmental panel on climate change (IPCC); what countries must do under the 2016 Paris Agreement; and predicting carbon emissions.
The students will also tour the National Assembly and the demilitarized zone at the inter-Korean border.
Paraguayan environment and sustainable development bureau official Adriana Orrego said the program would hopefully help him contribute to improving the measuring of carbon emissions in his country.
Jointly hosted by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the "Program on Greenhouse Gases" invited 33 environment officials, from countries in Asia, Africa, South America and Oceania.
The ministry's Greenhouse Gas Inventory and Research Center selected the participants through screening 348 candidates from 84 countries based on the candidates' academic and employment histories and IT skills.
The instructors are three Koreans and six from overseas, including those from the UNFCCC, the Austrian environment ministry and the RWA Group, an international group of experts in waste management, resource and energy efficiency.
The program teaches about measurement, reporting and verification (MRV) of carbon emissions in the sectors of energy, manufacturing, agriculture and waste; guidelines from the intergovernmental panel on climate change (IPCC); what countries must do under the 2016 Paris Agreement; and predicting carbon emissions.
The students will also tour the National Assembly and the demilitarized zone at the inter-Korean border.
Paraguayan environment and sustainable development bureau official Adriana Orrego said the program would hopefully help him contribute to improving the measuring of carbon emissions in his country.
Tuesday, July 16, 2019
Reading Monday: Trump’s vehicle emissions
President Trump’s administration has fought to roll back Obama-era vehicle emissions standards since his inauguration, and a final version of the looser rules is expected to be revealed later this summer. But since the rollback faces a number of obstacles — likely including a long, drawn-out battle in the court system that could ultimately kneecap the effort — the administration has found another way to discourage automakers from increasing the fuel efficiency of their vehicles: lower the fines for missing the targets.
Source: https://www.theverge.com/2019/7/15/20695407/trump-vehicle-emissions-rollback-fines-epa-nhtsa
Source: https://www.theverge.com/2019/7/15/20695407/trump-vehicle-emissions-rollback-fines-epa-nhtsa
Monday, July 8, 2019
Social Responsibility Management System to indicate gender inequality in 2019/2020
- Staff Data Module indicates newly hires / turning / working hours
- Position and Salary Module indicates in gender comparison
- Committee Module indicates Women in Leadership
- Parental leave: capture information on date of leave/return for male and female
Friday, June 28, 2019
UK to achieve net zero emissions by 2050
Britain made a legally binding commitment on Thursday to bringing all greenhouse gas emissions to net zero by 2050, setting it the first major economy in the world to pass laws to end its contribution to global warming by mid-century.
The target was more ambitious than the previous goal of cutting its greenhouse gases by at least 80 percent on 1990 levels by mid-century, which was enshrined in the Climate Change Act in 2008. The amendment of the 2050 goal, approved by the House of Commons and House of Lords this week, came into effect on Thursday.
The net zero target was recommended by the Committee on Climate Change, Britain's independent climate advisory body. It means any emissions would be balanced by schemes to offset an equivalent amount of greenhouse gases from the atmosphere, such as planting trees or using technology like carbon capture and storage.
Source: http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2019-06/28/c_138179264.htm
The target was more ambitious than the previous goal of cutting its greenhouse gases by at least 80 percent on 1990 levels by mid-century, which was enshrined in the Climate Change Act in 2008. The amendment of the 2050 goal, approved by the House of Commons and House of Lords this week, came into effect on Thursday.
The net zero target was recommended by the Committee on Climate Change, Britain's independent climate advisory body. It means any emissions would be balanced by schemes to offset an equivalent amount of greenhouse gases from the atmosphere, such as planting trees or using technology like carbon capture and storage.
Source: http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2019-06/28/c_138179264.htm
Wednesday, June 26, 2019
European Airports to cut carbon emissions to zero by 2050
European airports want to cut carbon emissions to zero by 2050 at the latest, Airports Council International (ACI)-Europe said June 26 as its members gathered in Limassol, Cyprus for its annual congress and general assembly.
ACI Europe said 194 airports run by 40 airport operators across 24 European countries had also individually committed to the same objective, marking “a step change in the climate action of the airport industry.”
It estimated that, based on current European airport traffic volumes—2.34 billion passengers in 2018—the commitment would eliminate 3.46 million tons of annual CO2 emissions as of 2050.
Continue Reading
Britain’s first hydrogen train
"Mini power stations on wheels", is how Alex Burrows from the University of Birmingham describes them.
He is the project director for the 'Hydroflex' train which was showcased at an event in the West Midlands.
Unlike diesel trains, hydrogen-powered trains do not emit harmful gases, instead using hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, water and heat.
It is "a fully green fuel", says Helen Simpson from rail rolling stock company Porterbrook, which created the Hydroflex in partnership with Birmingham University's centre for Railway Research.
Read more here: https://www.bbc.com/news/business-48698532
He is the project director for the 'Hydroflex' train which was showcased at an event in the West Midlands.
Unlike diesel trains, hydrogen-powered trains do not emit harmful gases, instead using hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, water and heat.
It is "a fully green fuel", says Helen Simpson from rail rolling stock company Porterbrook, which created the Hydroflex in partnership with Birmingham University's centre for Railway Research.
Read more here: https://www.bbc.com/news/business-48698532
Monday, June 24, 2019
READING MONDAY: Citi Hong Kong invests in renewable energy credits
READING MONDAY: Citi Hong Kong invests in renewable energy credits
Source: https://esg.theasset.com/ESG/37840/citi-hong-kong-invests-in-renewable-energy-credits-
Purchase of renewable energy certificates for 300,00 kWh of electricity puts Citi on track to meet environmental footprint goal of sourcing renewable power for 100 percent of its needs by 2020
By The Asset
ttt
Citi is taking an important step towards achieving its goal to source renewable power for 100 percent of its global electricity needs through the purchase of renewable energy certificates (RECs) from CLP Power Hong Kong Limited (CLP) and the Hongkong Electric Company, Limited (HK Electric). The investment equates to the purchasing of a combined 300,000 kWh of electricity generated by local renewable energy sources, making Citi the current top renewable energy certificate purchaser in the Hong Kong financial sector. These renewable energy resources are either generated or purchased by CLP and HK Electric, and include solar and wind power projects.
Continue reading
Source: https://esg.theasset.com/ESG/37840/citi-hong-kong-invests-in-renewable-energy-credits-
Purchase of renewable energy certificates for 300,00 kWh of electricity puts Citi on track to meet environmental footprint goal of sourcing renewable power for 100 percent of its needs by 2020
By The Asset
ttt
Citi is taking an important step towards achieving its goal to source renewable power for 100 percent of its global electricity needs through the purchase of renewable energy certificates (RECs) from CLP Power Hong Kong Limited (CLP) and the Hongkong Electric Company, Limited (HK Electric). The investment equates to the purchasing of a combined 300,000 kWh of electricity generated by local renewable energy sources, making Citi the current top renewable energy certificate purchaser in the Hong Kong financial sector. These renewable energy resources are either generated or purchased by CLP and HK Electric, and include solar and wind power projects.
Continue reading
Wednesday, June 19, 2019
NEW REGULATION IS COMING: EXCHANGE SEEKS VIEWS ON STRENGTHENING ESG RULES AND PUBLISHES GUIDANCE MATERIALS ON ESG AND GENDER DIVERSITY
NEW REGULATION IS COMING: EXCHANGE SEEKS VIEWS ON STRENGTHENING ESG RULES AND PUBLISHES GUIDANCE MATERIALS ON ESG AND GENDER DIVERSITY
The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (the Exchange), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited (HKEX), today (Friday) announces the publication of:
- Consultation Paper “Review of the Environmental, Social and Governance Reporting Guide and related Listing Rules” (ESG Consultation)
- ESG guidance materials (including e-training and Frequently Asked Questions Series 17 and 18); and
- Updated Guidance Letter HKEX-GL86-16 (i) setting out our expected disclosure on ESG matters and (ii) requiring disclosures on gender diversity in the listing documents of new applicants.
ESG Consultation
The key focus of the Exchange’s latest ESG Consultation is to support and improve issuers’ governance and disclosure of ESG activities and metrics.
“Our proposals emphasise the board’s leadership role and accountability in ESG and the governance structure for ESG matters. The consultation also seeks to highlight that materiality in respect of ESG is key to meaningful and concise reporting. Our proposal to require disclosure on climate-related issues echoes the increasing international focus on climate change and its impact on businesses,” said David Graham, HKEX’s Head of Listing.
This consultation reflects the Exchange’s commitment to enhance ESG reporting and disclosure by listed companies, and builds upon its ongoing ESG-related efforts since the launch of the ESG Reporting Guide in 2013.
Key proposals:
- Introducing mandatory disclosure requirements in the ESG Reporting Guide to include:
- a board statement setting out the board’s consideration of ESG issues; and
- applications of relevant reporting principles and boundaries in the ESG report;
- Requiring disclosure of significant climate-related issues which have impacted and may impact the issuer;
- Amending the “Environmental” key performance indicators (KPIs) to require disclosure of relevant targets;
- Upgrading the disclosure obligation of “Social” KPIs to “comply or explain”; and
- Shortening the deadline for publication of ESG reports to align with the publication timeframe of the annual report (ie within four months (Main Board issuers) or three months (GEM issuers) after the year-end date).
The deadline for responding to the ESG Consultation is 19 July 2019.
Interested parties are encouraged to respond to the ESG Consultation by completing and submitting the questionnaire.
ESG Guidance Materials
E-training: To reinforce the focus of the ESG Consultation, the Exchange has launched an e-training course, “ESG Governance and Reporting”, which explains the board’s leadership role in ESG matters and covers the following six topics:
- What is ESG, and why is it important
- Board’s role in ESG governance
- Why report on ESG
- Essential elements in an ESG report
- Details on ESG reporting
- ESG disclosure by IPO applicants
The e-training takes approximately 45 minutes to complete.
Tuesday, June 18, 2019
Shipping load decisions in Bank will include CO2 emission measures
Shipping load decisions in Bank will include CO2 emission measures
International shipping accounts for 2.2% of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and the U.N.’s International Maritime Organization (IMO), has a long-term goal to cut greenhouse gas emissions by 50% from 2008 levels by 2050. Banks will for the first time include efforts to cut carbon dioxide emissions in their decision making when providing shipping company loans.Source: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-shipping-environment-banks/banks-to-include-co2-emission-measures-in-shipping-loan-decisions-idUSKCN1TI2W4
Monday, June 17, 2019
READING MONDAY: Bitcoin leaves a carbon footprint as large as Las Vegas, study finds
READING MONDAY: Bitcoin leaves a carbon footprint as large as Las Vegas, study finds
Source: https://edition.cnn.com/2019/06/14/tech/bitcoin-carbon-footprint-trnd/index.htmlA new study found that the cryptocurrency Bitcoin requires a lot of electricity, leaving a significant carbon footprint -- one that rivals the environmental impact of Las Vegas or a small country like Sri Lanka.
Each year, Bitcoin generates about 22 megatons in CO2 emissions, the researchers estimate.
Saturday, June 15, 2019
Reading: IKEA shows sustainability can be colorful, motivating and enjoyable
IKEA shows sustainability can be colorful, motivating and enjoyable
Source: https://www.designboom.com/design/ikea-democratic-design-days-sustainability-urbanization-06-12-2019/images of massive stores and mass-produced items might come to mind when you first think of IKEA, but sustainability is a key driving force behind every action they take and every product they make. in fact, when witnessing all their announcements like ‘ROGNON‘, ‘SAMMANLÄNKAD‘ and ‘urban village project’ from the brand’s democratic design days 2019 event, it is clear to see how devoted they are to sustainability, especially in the age of urbanization. ‘IKEA is an every-growing company so if we want to achieve our sustainability strategy, then we really need to reset everything from materials to production to transportation,’ begins lena pripp-kovac, head of sustainability, inter IKEA group.
launched in 2012 and updated in 2018, ‘people & planet positive’ is IKEA’s sustainability strategy and encompasses everything within their own franchise as well as their value chain. two of their most notable and ambitious aims are to remove single use plastic by 2020, and use only renewable or recyclable materials by 2030.
Continue Reading here
Friday, June 14, 2019
Reading: Why The Circular Economy Will Not Fix Fashion's Sustainability Problem
Why The Circular Economy Will Not Fix Fashion's Sustainability Problem
Source: https://www.forbes.com/sites/gulnazkhusainova/2019/06/12/why-the-circular-economy-will-not-fix-fashions-sustainability-problem/#5f4bff4d4d05Fashion has a sustainability problem. In 2015 the industry was responsible for the emission of 1,715 million tons of CO2. It’s about 5.4% of the 32.1 billion tons of global carbon emissions and just second after the oil and gas industry. Global apparel and footwear consumption are expected to nearly double in the next 15 years–and so its negative impact on the environment.
Continue Reading
Tuesday, June 11, 2019
SGX Sustainability Reporting Guide
1. Introduction
1.1 Listing Rule 711A requires every listed issuer to prepare an annual sustainability report, which must describe the issuer's sustainability practices with reference to the primary components set out in Listing Rule 711B on a 'comply or explain' basis. This Practice Note contains the Sustainability Reporting Guide (the "Guide"), which provides guidance on the expected structure and contents and the preparation of the sustainability report.
1.2 Sustainability reporting disclosure does not detract from the issuer's obligation to disclose any information that is necessary to avoid the establishment of a false market in the issuer's securities or would be likely to materially affect the price or value of its securities pursuant to Listing Rule 703.
1.3 A glossary of the common terms used in the Guide is set out in paragraph 7 of this Guide.
Thursday, June 6, 2019
SDG 12 - Monitoring of Solid Waste in Hong Kong
According to the report "Monitoring of Solid Waste in Hong Kong", published by the Environmental Protection Department of the HKSAR Government in December 2018, over 5.7 million tonnes of waste are generated every year in Hong Kong, of which almost 70% ends up in landfills. The brand new exhibition at the Museum’s Hong Kong Jockey Club Green Gallery presents major initiatives of The Hong Kong Jockey Club that have helped pioneer new thinking on how to protect the environment in the local community. With the aid of multimedia interactive exhibits, the exhibition promotes United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 12 – Responsible Consumption and Production – and aims to inspire the visitors to get involved in waste-reduction action and to live a green lifestyle.
Learn more from: https://www.cpr.cuhk.edu.hk/en/press_detail.php?id=3041&t=cuhk-jockey-club-museum-of-climate-change-launches-responsible-consumption-and-waste-reduction-exhibition-at-the-hong-kong-jockey-club-green-gallery&id=3041&t=cuhk-jockey-club-museum-of-climate-change-launches-responsible-consumption-and-waste-reduction-exhibition-at-the-hong-kong-jockey-club-green-gallery
Learn more from: https://www.cpr.cuhk.edu.hk/en/press_detail.php?id=3041&t=cuhk-jockey-club-museum-of-climate-change-launches-responsible-consumption-and-waste-reduction-exhibition-at-the-hong-kong-jockey-club-green-gallery&id=3041&t=cuhk-jockey-club-museum-of-climate-change-launches-responsible-consumption-and-waste-reduction-exhibition-at-the-hong-kong-jockey-club-green-gallery
Wednesday, June 5, 2019
Chew’s Agriculture - Singapore’s first SME sustainability-linked loan
DBS today announced that Chew’s Agriculture, a leading egg producer in Singapore, has signed a 10-year, SGD 27 million sustainability-linked loan with the bank. This marks a milestone for sustainable development in Singapore – it is the nation’s first sustainability-linked loan for an SME.
The loan was evaluated based on a series of environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance metrics. Chew’s will use the loan for the construction of a new farm with larger cage-free facilities so that hens[1] which lay eggs on the farm will continue to be housed in the most optimum conditions, such as larger litter areas and elevated perches.
Complete story : https://www.dbs.com/newsroom/Chews_Agriculture_signs_Singapores_first_SME_sustainability_linked_loan_with_DBS
The loan was evaluated based on a series of environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance metrics. Chew’s will use the loan for the construction of a new farm with larger cage-free facilities so that hens[1] which lay eggs on the farm will continue to be housed in the most optimum conditions, such as larger litter areas and elevated perches.
Complete story : https://www.dbs.com/newsroom/Chews_Agriculture_signs_Singapores_first_SME_sustainability_linked_loan_with_DBS
Tuesday, June 4, 2019
High Performance Environmental Management System with Self Serving Data Input
The Consumption Resources in EMS Environmental Management System
- More than 1000 physical locations
- Over 200 active login users
- More than 60 countries accessing instance
- Over 10000 bill records annually
- Over 150 reports for more 10 functional departments
- SDGs target report
- Bill Records for Electricity, Water, Gas, Fuel
- Recycled Paper management and Business flight travel management
- APIs support system integration
The Electricity Resource lets you update and create Electricity Consumption in a EMS instance. You can use consumption units and emission units to create or update different unit of the same consumption. You can also add or update product pdf.
The EMS's Electricity Consumption API lets you do the following with the Electricity resource. More detailed versions of these general actions may be available.
Want to know more? Request a Demo today
Monday, June 3, 2019
Carbon Emission when business travel
Business travel
Greenhouse Gas and Carbon Emission can be affected by fuel consumption, travel cabin class and length of the jourary. It is more green if you travel in economy, newer aircraft and usage of biofuel.A very useful tool from Cathy Pacific - Fly Greener Carbon Emission Calculator
https://www.cathaypacific.com/cx/en_MM/about-us/environment/fly-carbon-neutral-fly-greener/calculate-and-offset-your-carbon-emissions.htmlTuesday, May 28, 2019
SDG 6 clean water and sanitation Environment Management System EMS - Water Consumption Monitoring Waste Consumption Monitoring
Environment Management System EMS on SDG 6
How to keep track SDG 6
- clean water and sanitation with Ideo Concepts's Environment Management System EMSWater Consumption Monitoring
- total water consumption and its intensityWaste Consumption Monitoring
- total number of hazardous and non-hazardous waste produced and how they are handled byReporting on consumption/emission
- Plus reporting engine data mining on the consumption and CO2-E emission.Monday, May 27, 2019
17 SDGs Which you interest?
Goal 1: No poverty
Goal 2: Zero hunger
Goal 3: Good health and well-being for people
Goal 4: Quality education
Goal 5: Gender equality
Goal 6: Clean water and sanitation
Goal 7: Affordable and clean energy
Goal 8: Decent work and economic growth
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
Goal 10: Reducing inequalities
Goal 11: Sustainable cities and communities
Goal 12: Responsible consumption and production
Goal 13: Climate action
Goal 14: Life below water
Goal 15: Life on land
Goal 16: Peace, justice and strong institutions
Goal 17: Partnerships for the goals
More information from: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/
Goal 2: Zero hunger
Goal 3: Good health and well-being for people
Goal 4: Quality education
Goal 5: Gender equality
Goal 6: Clean water and sanitation
Goal 7: Affordable and clean energy
Goal 8: Decent work and economic growth
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
Goal 10: Reducing inequalities
Goal 11: Sustainable cities and communities
Goal 12: Responsible consumption and production
Goal 13: Climate action
Goal 14: Life below water
Goal 15: Life on land
Goal 16: Peace, justice and strong institutions
Goal 17: Partnerships for the goals
More information from: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/
Environment Management Dashboard (updated!) - KPI Monitoring
Environment Management Dashboard - KPI Monitoring
Monitoring of resources consumption on a per-location basis, consumption types include :-
- Electricity Consumption
- Fuel Consumption
- Gas Consumption
- Lubricant / Refrigerant Consumption
- Flight/Travel consumption records Multi Legs
Collection of Waste Management data
Reporting on consumption and cost
Reporting on CO2 Emission
Record and Document Management on
- Investments in Environmental Projects
- Environmental Issues and Non Compliance Records
- Training Records
- Environmental Audits
Multi Shop / Location Support.
Centralized Enterprise Data into platform and multi-dimensional reporting tools for advance user.
See more on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/ideoconceptshk/
See more on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/ideoconceptshk/
Sunday, May 19, 2019
COOL TOY: DRONES TO MONITOR EMISSIONS FOR SHIPPING/SEA FREIGHT TRANSPORT
It is cool: DRONES TO MONITOR RISING EMISSIONS FROM SHIPPING
Hong Kong is gearing up to use drones to monitor emissions from ships.
Highly efficient sensors developed after a series of extensive trials have been fitted on the drones. In real time, they accurately measure the pollution content present in the smoke plume released by a ship.
When equipped, the drones, developed by a team of researchers from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), scan emissions by hovering over ships for just two minutes.
Continue reading...........
Source: https://ienv.ust.hk/news/cgtn-drones-monitor-rising-emissions-shipping
Hong Kong is gearing up to use drones to monitor emissions from ships.
Highly efficient sensors developed after a series of extensive trials have been fitted on the drones. In real time, they accurately measure the pollution content present in the smoke plume released by a ship.
When equipped, the drones, developed by a team of researchers from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), scan emissions by hovering over ships for just two minutes.
Continue reading...........
Source: https://ienv.ust.hk/news/cgtn-drones-monitor-rising-emissions-shipping
Saturday, May 18, 2019
Shanghai car emissions
According to the new VI B standard, the carbon monoxide emission of cars should not exceed 500 mg/km, and the oxynitride emission should not exceed 35 mg/km.
Source: https://news.metal.com/newscontent/100925008/shanghai-to-intensify-car-emissions-standards-in-jul/
Source: https://news.metal.com/newscontent/100925008/shanghai-to-intensify-car-emissions-standards-in-jul/
Friday, May 17, 2019
IDEO CONCEPTS'S PROQUALI Advanced Inspection/Audi Management System - third party inspection / audit companies, buying offices and retailers solution
PROQUALI Advanced Inspection/Audi Management System
PROQUALI Advanced Inspection/Audi Management System is a all-in-one soluation application for managing Inspection and Audits. The features of Advanced Inspection/Audi Management System can be supported by third party inspection / audit companies, buying offices and retailers.With the IDEO CONCEPTS'S PROQUALI Advanced Inspection/Audi Management System, the key benefits to all parties are: Reduce exchange of emails, Central Data Repository, Facilitate Cloud based workflow, High level prospective for management.
Key features included:
- Company Master Database
- Service Master Database
- Payment/Account Management
- Job/Task Sehceduling Calendar
- Task Management/List Manage
- Advanced Report Builder
- Advanced Document Management
- Client’s Portal
- Job Booking
- Report/Data Analysis Reporting tool
- Advanced Document Download
Thursday, May 16, 2019
SDG 12 responsible consumption and production - Air Emission - Sulphur Oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM) and carbon dioxide (CO2)
Sulphur Oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are emitted to the atmosphere. Collectively, ship generated emissions can be significant in areas subject to heavy marine traffic leading to concerns regarding air quality, bot at local level, in coastal areas, or in a more global level, regarding to CO2 emissions leading to Greenhouse Gas emissions and contributing to global warming. Tracking and Monitoring by Environmental Management System EMS is necessary for SME.
With Air Management Module, Material Monitoring Module, Waste Monitoring Module, amount of emission with ghg scope summary reporting will be generated with friendly chart system automatically.
Features of Environmental Management System - Environmental Features - SDG Goal 1-17 can be achieved
p.s. PROGRESS OF GOAL 12 IN 2018
Decoupling economic growth from resource use is one of the most critical and complex challenges facing humanity today. Doing so effectively will require policies that create a conducive environment for such change, social and physical infrastructure and markets, and a profound transformation of business practices along global value chains.
The per capita “material footprint” of developing countries grew from 5 metric tons in 2000 to 9 metric tons in 2017, representing a significant improvement in the material standard of living. Most of the increase is attributed to a rise in the use of non-metallic minerals, pointing to growth in the areas of infrastructure and construction.
For all types of materials, developed countries have at least double the per capita footprint of developing countries. In particular, the material footprint for fossil fuels is more than four times higher for developed than developing countries.
By 2018, a total of 108 countries had national policies and initiatives relevant to sustainable consumption and production.
According to a recent report from KPMG, 93 per cent of the world’s 250 largest companies (in terms of revenue) are now reporting on sustainability, as are three quarters of the top 100 companies in 49 countries.
With Air Management Module, Material Monitoring Module, Waste Monitoring Module, amount of emission with ghg scope summary reporting will be generated with friendly chart system automatically.
Features of Environmental Management System - Environmental Features - SDG Goal 1-17 can be achieved
p.s. PROGRESS OF GOAL 12 IN 2018
Decoupling economic growth from resource use is one of the most critical and complex challenges facing humanity today. Doing so effectively will require policies that create a conducive environment for such change, social and physical infrastructure and markets, and a profound transformation of business practices along global value chains.
The per capita “material footprint” of developing countries grew from 5 metric tons in 2000 to 9 metric tons in 2017, representing a significant improvement in the material standard of living. Most of the increase is attributed to a rise in the use of non-metallic minerals, pointing to growth in the areas of infrastructure and construction.
For all types of materials, developed countries have at least double the per capita footprint of developing countries. In particular, the material footprint for fossil fuels is more than four times higher for developed than developing countries.
By 2018, a total of 108 countries had national policies and initiatives relevant to sustainable consumption and production.
According to a recent report from KPMG, 93 per cent of the world’s 250 largest companies (in terms of revenue) are now reporting on sustainability, as are three quarters of the top 100 companies in 49 countries.
Wednesday, May 15, 2019
How Ideo Concepts' Environment Management System (EMS) works - Measuring and Managing CALCULATION METHOD CO2 Emission from Freight Transport Operations
How Ideo Concepts' Environment Management System (EMS) works - Measuring and Managing CALCULATION METHOD CO2 Emission from Freight Transport Operations
Activity-based approach (calculation method recommended for use by chemical companies)
CO2 emissions = Transport volume by transport mode x average transport
distance by transport mode x average CO2-emission factor per
tonne-km by transport mode
[Tonnes CO2 emissions = tonnes x km x g CO2 per tonne-km / 1.000.000]
Energy-based approach (calculation method recommended for use by transport companies)
CO2 emissions = fuel consumption x fuel emission conversion factor [Tonnes CO -emissions = liters x kg CO2 per liter fuel / 1.000]
Learning from: https://www.ecta.com/resources/Documents/Best%20Practices%20Guidelines/guideline_for_measuring_and_managing_co2.pdf
Good and Bad. Dutch CO2 emissions fall in 2018 2020 Target
Dutch greenhouse gas emissions in 2018 fell by 2.2 percent to 189.5 billion kg of carbon dioxide and equivalents helped by lower emissions by power companies, the country’s statistical office said on Thursday.
Emissions were down 14.5 percent from 1990 levels, Statistics Netherlands said, meaning the country is unlikely to meet its Kyoto Protocol goal of a 25 percent reduction by 2020.
Source: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-netherlands-pollution/dutch-co2-emissions-fall-in-2018-still-far-from-2020-goal-idUSKCN1SF0K4
Emissions were down 14.5 percent from 1990 levels, Statistics Netherlands said, meaning the country is unlikely to meet its Kyoto Protocol goal of a 25 percent reduction by 2020.
Source: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-netherlands-pollution/dutch-co2-emissions-fall-in-2018-still-far-from-2020-goal-idUSKCN1SF0K4
Tuesday, May 14, 2019
Collaborate and share best-practice to optimise SDG action
Cross-sector collaboration is an area of opportunity that corporates are seemingly failing to capitalise on. Research shows that 70% of sustainability professionals are seeking to collaborate, but less than half have been offered any opportunities to do so. Meanwhile, the number of companies “actively involved” in collaborations linked to the SDGs has fallen to a third, down 7% from last year.
Source: https://www.edie.net/library/Five-steps-to-take-the-lead-on-the-Sustainable-Development-Goals/6807
Source: https://www.edie.net/library/Five-steps-to-take-the-lead-on-the-Sustainable-Development-Goals/6807
Highest CO2 Level in Human HIstory 415 ppm
Carbon dioxide levels hit new landmark at 415 ppm, highest in human history
Source: https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2019/05/13/climate-change-co-2-levels-hit-415-parts-per-million-human-first/1186417001/
Data from the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii showed that carbon dioxide levels surpassed 415 parts per million on Friday. https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/obop/mlo/
Saturday, May 11, 2019
Customized Dashboard in Environmental Management System EMS
Customized Dashboard helps organizations get a clear view of the performance of their business. But, some dashboards do a better job of that than others in organization. With Customized dashboards, we can easily send alerts and require follow up. For example, if a region’s emission raise above a certain threshold, that related manager should receive an alert with all associated metrics and be required to submit an associated action plan. As you build dashboards at the individual emission level, you should also report on the key alert level of business.
Friday, May 10, 2019
Hong Kong scores "C-" on the first Paris Watch - Hong Kong Report Card 2019
Hong Kong scores "C-" on the first Paris Watch - Hong Kong Report Card 2019. Hong Kong received an overall C- rating in terms of its performance on reducing carbon emissions and enhancing energy efficiency, the responsibilities it needs to shoulder as member of C40.
Source: http://www.ccinnolab.org/upload/files/Paris%20Watch%20%E2%80%93%20Hong%20Kong%20Report%20Card%202019.pdf
https://www.ccinnolab.org/tc/Events/28
Source: http://www.ccinnolab.org/upload/files/Paris%20Watch%20%E2%80%93%20Hong%20Kong%20Report%20Card%202019.pdf
https://www.ccinnolab.org/tc/Events/28
HK sounds out investors for 'green bond' issuance
Hong Kong expects to attend a series of investor meetings in relation to a proposed green bond offering. Subject to market conditions, a US dollar-denominated green bond offering may follow, an announcement said.
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority, the representative in the potential green bond offering, unveiled three measures to support and promote Hong Kong’s green finance development today.
Wednesday, May 8, 2019
Sustainable Development Goals
Sustainable Development Goals
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015, provides a shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future. At its heart are the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which are an urgent call for action by all countries - developed and developing - in a global partnership. They recognize that ending poverty and other deprivations must go hand-in-hand with strategies that improve health and education, reduce inequality, and spur economic growth – all while tackling climate change and working to preserve our oceans and forests.
Tuesday, May 7, 2019
Supporting UN SDGs
On September 25th 2015, the UN general assembly adopted a set of goals to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all as part of a new sustainable development agenda. Each goal had specific targets to be achieved over the next 15 years. These 17 goals comprising 169 targets are part of an ambitious global plan to transform our world economically, socially, and environmentally
Sustainable Development
What is Sustainable Development?
Sustainable Development means "development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." ["Our Common Future", 1987, the World Commission on Environment and Development]
The goal of sustainable development is to strike a balance between the needs of the environment, society and economy in order to maintain a quality standard of life for both present and future generations.
Sustainable Development in Hong Kong
A sustainable future for Hong Kong would require a change of our mindset to achieve economic and social development with conservation of the environment.
It requires all sectors of the community to work hand in hand in order to achieve a sustainable future for Hong Kong. There are many ways in which you can get involved. You can contribute to sustainability by reducing energy consumption, using less water, and reducing waste.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)